World History Class 08
A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS AND Q&A SESSION (05:08 PM)
NAPOLEAN'S FOREIGN POLICY (05:22 PM)
- It was more influenced by his personal ambition to rule Europe and partly by revolutionary ideas. Austria formed a coalition with Sardinia & Prussia, against Napolean when he was defeated by Nelson in the Battle of Nile. Napoleon defeated the Austrians and Sardinians and he could win the support of Sweden and Russia against England.
- When Nelson of England defeated Sweden, both Sweden and Russia withdrew their support for Napolean.
- Diplomatically, Napolean signed the "Treaty of Amiens" with England and ended the war, however, his main purpose was to strengthen his position against England. Secretly he made an attempt to occupy Belgium, a friendly country of England. He also tried to win the support of Indian princes against England.
- In the fresh rivalries started, Napolean was defeated by Nelson of England in the "Battle of Trafalgar, 1804", however, Nelson died in the battle.
- As Napolean was defeated, Austria again formed a coalition with Prussia, and Russia against Napolean. Napoleon defeated the Austrians and entered Prussia. The defeat of Austria made England's prime minister, William Pitt, to remark "Roll up the map of Europe, It is not required for another 10 years".
- Napolean defeated the Prussians in the "Battle of Jena". He celebrated his coronation festival as Emperor of France in Berlin.
- He defeated the Russians in the "Battle of Britenfields" and forced the Czar of Russia to sign Tilsit Treaty. The treaty marked the highest stage of Napolean's power, he had entire Europe at his feet except England.

CONTINENTAL SYSTEM (06:21 PM)
- It means a policy of total blockade of England from the rest of the world. In other words, it is a policy of isolating England. Under the policy, sanctions were imposed against England.
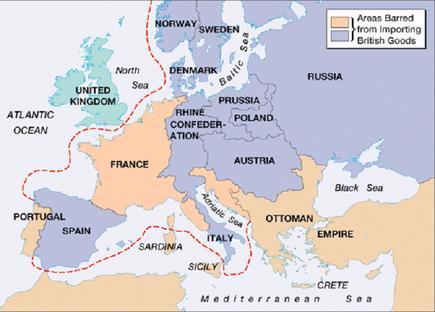
- It started with the "Berlin Decrees" passed by Napolean in Berlin. Under the policy, no country to trade with England. Both Import and Export trade with England was banned. Countries cooperating with England were threatened. England accepted the challenge and passed "orders-in-council".
- Continental system was a grave mistake committed by Napolean for the reasons
- a) France had no Naval strength to implement and enforce the continental system against England.
- b) Europe was dependent on England for essential goods like Textiles, leather products, and tea & coffee.
- c) All along the sea coast of France, Smuggling started and France became the first country affected. France was the major exporter of corn to England and France became the first country to violate the continental system.
- d) Portugal was the first European country to revolt against the continental and it was supported by England. Even the pope questioned the continental system and was threatened by Napolean offending the sentiments of Catholics.
- To punish Portugal, Napolean decided to enter Portugal via Spain. Spain as a country revolted against Napolean, not allowing the French army. Egocentric Napolean remained in Spain without any progress with a Six lakh army. It is said that it was a "Spanish Ulcer" that ruined Napolean just as a "Deccan Ulcer" ruined Aurangzeb.
- When Russia withdrew from the continental system, Napolean went to war with Russia and it ended up as a disaster.
- Austria formed the 4th coalition with the support of all European countries against Napolean. In the "Battle of Libzig" also called the "Battle of Nations", Napolean was defeated and imprisoned on the island of Elba.
- Napolean escaped from Elba by swimming in the sea and he returned back to Paris. The fifth coalition was formed in the "Battle of Waterloo", Napolean was caught and he was imprisoned at Helena where he died in 1821.
REASONS FOR THE DOWNFALL OF NAPOLEAN (06:43 PM)
- He never recognized the limitations of human energy. For him, nothing was impossible
- He was essentially a powermonger. Highly egocentric Napolean never allowed nationalism to survive against his will.
- In the name of liberating the countries from monarchies, he finally established his own empire.
- He used the resources of Italy and Germany (Prussia) for the construction activities in France.
- The empire he built was built by force, not by the willing cooperation of the people, he appointed his brothers Joseph and Loui as the rulers, undermining the spirit of nationalism.
- For all these reasons it is said that "Napolean's empire was destined to be doomed for its internal contradictions".
NAPOLEAN- CHILD OF REVOLUTION?- CRITICAL ASSESSMENT
- Napolean declared himself a child of the revolution.
- It is a highly disputed matter between his admirers and adversaries.
- He was not the child of revolution for the reasons:
- He denied liberty, the first slogan of revolution. For him, the ''French wanted equality but not liberty.''
- Even his concept of equality is superficial. He was not bothered about creating conditions favorable for enjoying equality.
- The concept of Fraternity was blatantly violated.
- In the name of liberating the people and spreading revolutionary ideas he created an empire of his own and satisfied his imperialistic desires.
- Never respected the nationalism of Italians and Germans, and used their resources and war prisoners for his public works.
- However, there are equally valid reasons to call him a child of the revolution:
- He captured power while the revolution was passing through a crisis.
- He gave stability, prosperity, power, and prestige to disturbed France.
- Napoleon saved the French Revolution from external threats, particularly threats from Austria and Prussia.
- It was he who spread the revolutionary ideas into different parts of Europe.
- He introduced liberal reforms and his 'Code De Napolean' in the newly conquered territories.
- He once and for all ended the medieval concept of the ''Holy Roman Empire'' and liberated people from the absolutism and autocracy of Austria and Prussia.
- He heralded a new age characterized by the struggle between the forces of conservatism and progressivism.
- It was he who gave peace and stability to disturbed revolutionary France.
- Some more arguments from the supporter of the idea
- He liberated Italians and Germans from the control of Austria. [* German and Italian unification was the result of Napolean's war]
- Definitely, he heralded a new age characterized by a clash between the conservatism of the monarchy and the progressivism of the people of Europe in General.
- His legacy continued to decide the course of the history of Europe even after his death.
- It was Napolean who gave the masses the weapon of Constitutionalism and liberalism against the monarchies. And after his death also, his ideas continued to inspire Europe till the 1870s
- In this regard, he definitely deserves to be called as the Child of Revolution.
EFFECTS OF FRENCH REVOLUTION- INTERNAL & EXTERNAL (07:13 PM)
- Impact on France
- The ancient regime/ Age old social and political system in France was dismantled with French Revolution
- It ended Feudalism. Republicanism started in France
- Middle class took the leadership
- Slavery was banned
- Taxation system was rationalized- "Tax according to ability"
- Religion lost its vitality, State was upheld as the most powerful. Religion is subordinated to State.
- France understood the importance of Human rights.
- France understood the importance of Liberty and Equality.
- France became the first European country to have a written constitution.
- Impact on the world
- Great ideas such as Universalism got importance. [* Same is in India also in the form of "Sarve bhavantu sukhinah bhavantu"]. [** Universalism= for humanity, all mankind, thinking in terms of universe]
- Romanticism was replaced with the Scientific approach [* Romaticism= What that is not real, one wants to be real. Wanting a society without hunger, poverty, starvation, and inequality is romanticism.]
- [* Rousseau- "Man is born free and everywhere he is in chains"]
- [* Karl Marx- "Workers of the world unite; you have nothing to lose but your chains"]
- In the French Revolution, mobs could not capture power and were sidelined by the Middle class. In the Russian Revolution, peasantry gained power thus Russian Revolution was the LOGICAL END of the French Revolution.
- 1810- Spanish revolution, 1830- July revolution
- It inspired Italian unification, German unification
- After the Fall of Napolean, Vienna Treaty was signed in 1815. It has 4 principles- Balance of power, Compensation, Legitimacy, and Restoration
- Different parts of Europe were demanding constitutionalism.
COLONIALISM AND IMPERIALISM (07:27 PM)
- Imperialism
- It is a much older concept. It was evident in Ancient times.
- Characteristics of Imperialism
- a) Exhibiting the might/ power/ Strength and threatening the country. [* Contemporary- China threatening Taiwan and violating Air Space]
- b) A foreign power conquers or occupies another other country. But, It may or may not rule. [* Sending strong signals to the other country]
- c) One may conquer, and may rule but will not interfere in the native country's culture, economy, and society and will confine only to the administration.
- Example- Samudragupta defeated six Aryavartas, and liberated 18 forest kingdoms, but did not occupy that kingdom. The purpose was to show strength. Thus Guptas are called Imperial Guptas.
- In modern times, Imperialism assumed a different dimension. Earlier it was only about controlling polity. Now it took different dimensions such as financial imperialism and Cultural imperialism.
- Financial Imperialism- Controlling or regulating the finances [* Contemporary- Chinese checkbook diplomacy and Debt trap policy through liberal debt and loans and later trapping the countries in Debt. Chinese giving liberal debt to Srilanka, Pakistan, Iran, etc]
- Cultural imperialism- Giving importance to a particular culture. Example- Pan-Americanism. [* Contemporary- Chinese imposition of culture and language in Tibet].
- All three dimensions of Imperialism do not operate at a time.
- Colonialism
- It was the result of the Industrial Revolution.
- One country not only occupies the other, Rules, and administers but also brings a change in society, polity, economy, culture, religion, etc.
- It strikes at the very root of the identity.
- Colonialism operates all the scope of imperialism at a time.
- Colonialism differs from country to country, place to place, and Time to time as per the changing requirements of colonial power
- a) Place to place- Colonialism by Britain in White colonies V/S the colonial policy in Africa and India. Britain gave autonomy and self-governance in the colonies of Australia, New Zealand, and Canada while the same was denied to India.
- b) Time to time- England exported the raw material from India to Britain. It also meant, Exporting the raw materials + Sending the manufactured products to India. It also meant, Introduction of revenue systems and exploiting the resources. It also meant a Systematic policy to destroy all the industries such as the Shipbuilding industry, Textile industry, etc. It also meant, establishing the modern industry such as Railway to further exploit.
- Concept of colonialism was changing as per the requirements of colonial power.
The topic for the next class- is Colonliasm and Imperialism, the process of colonization.